Settings Page
The Settings page allows users to configure device parameters, advanced options, and the software appearance. It is divided into three tabs: Device, Advanced, and Appearance.
The Settings page in TQT Nuclei is where users can fine-tune the operational parameters of the NMR device, adjust advanced processing configurations, and customize the application’s appearance. The page is divided into three horizontal subpages: Device, Advanced, and Appearance. Each subpage provides specialized settings that give users full control over their NMR experiments and interface.
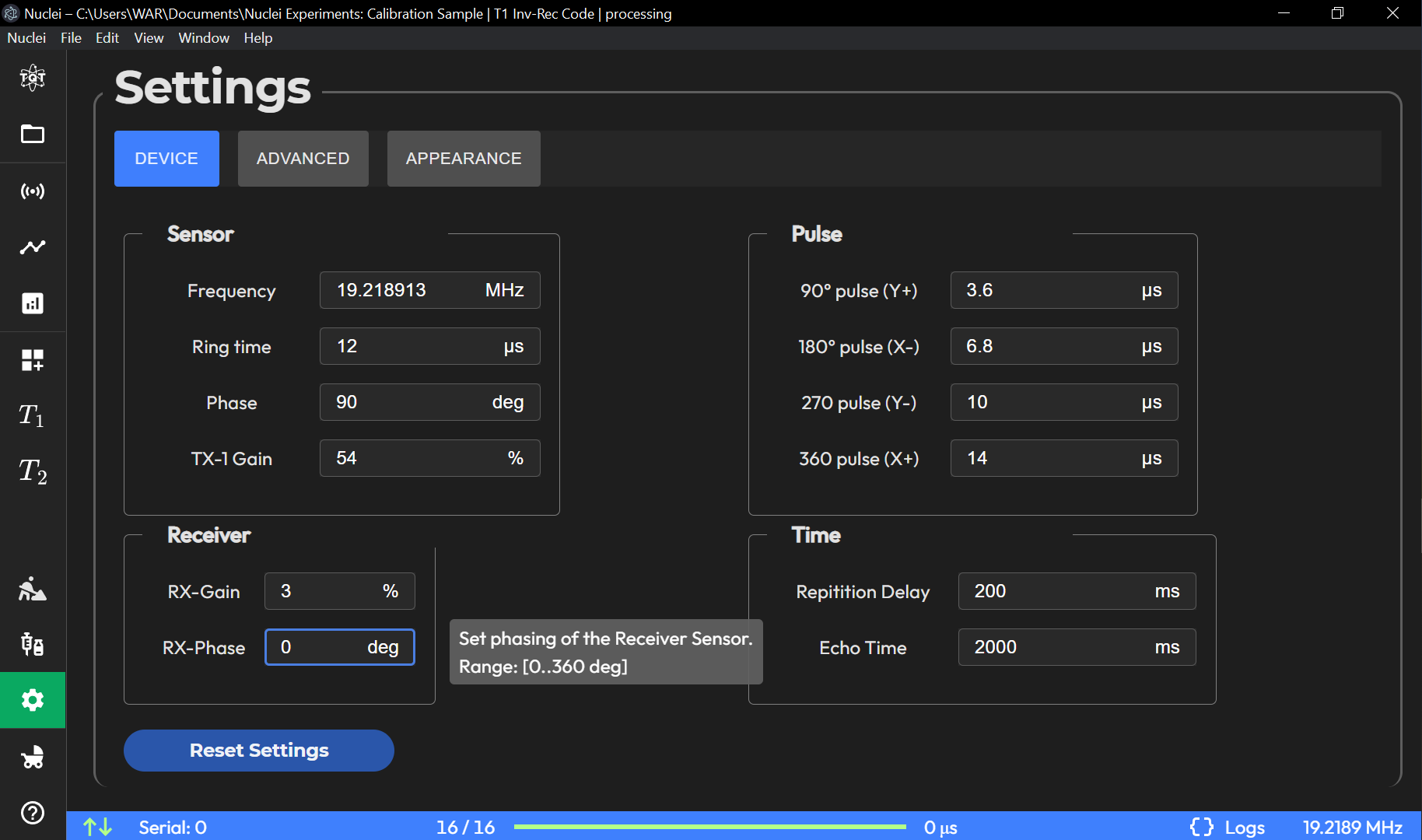
Device Subpage
The Device subpage contains core operational settings that control the behavior of the NMR device. These settings are essential for configuring the experiment environment and ensuring accurate measurements.
Frequency:
This field allows you to adjust the frequency of the NMR experiment to match the Larmor frequency of the nuclei being studied. Ensuring the correct frequency is critical for accurate resonance conditions.
Ring Time:
Also known as the dead time, this setting controls the time during which the system is not acquiring signals immediately after a radiofrequency pulse. This helps avoid detecting unwanted noise from the ringing of the resonant circuit.
Phase:
Adjusts the phase of the signal relative to the reference. Correct phase settings ensure that the acquired signals are in phase with the excitation pulses, improving the signal-to-noise ratio.
Tx-1 Gain:
The gain applied to the transmitter during excitation pulses. Adjust this setting to control the power delivered to the sample during radiofrequency pulses.
Rx Gain:
The gain applied to the receiver during signal acquisition. This setting controls the sensitivity of the NMR receiver and affects the signal amplification.
Rx Phase:
Controls the phase of the received signal. Adjustments here help in aligning the received signal for optimal phase detection.
P90_us, P180_us, P270_us, P360_us:
These fields specify the duration (in microseconds) of the 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360° pulses, respectively. These parameters must be finely tuned for accurate pulse sequences and depend on the specific sample and experimental setup.
Repetition Delay:
The time delay between successive scans. The global repetition delay is automatically set to 5 times the anticipated T1 relaxation time, but it recalculates whenever the anticipated relaxation rate is updated.
Echo Time:
This base value is used across all experiments to define the spacing between echoes in pulse sequences such as CPMG. Proper echo time selection is crucial for obtaining accurate spin-spin relaxation measurements.
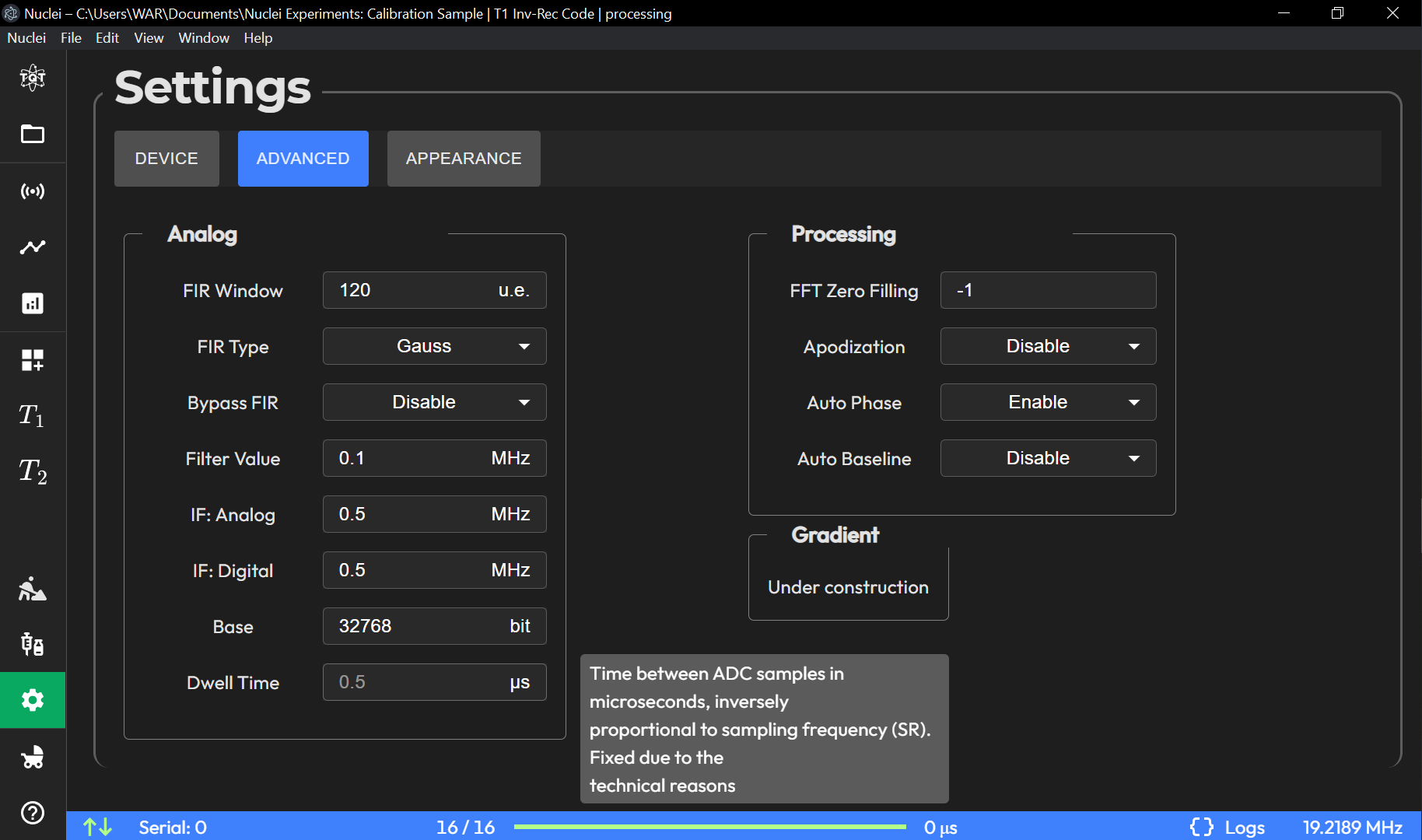
Advanced Subpage
The Advanced subpage offers a range of more technical settings related to signal filtering, intermediate frequency (IF) handling, and data processing. These settings allow users with more in-depth knowledge of NMR or signal processing to fine-tune their experiments.
FIR Window (1..512 units):
Specifies the length of the Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter window. A longer window improves frequency resolution but at the cost of time resolution.
FIR Type (Gauss | Sync):
Choose the type of FIR filter to apply to the acquired signal. Gauss and Sync filters have different characteristics, with Gauss providing smoother filtering and Sync offering sharper transitions.
Bypass FIR:
A boolean option that allows users to bypass the FIR filtering process entirely. Useful when raw, unfiltered data is required.
Filter Value (e.g. 0.1 MHz):
Sets the cutoff frequency for filtering out high-frequency noise from the signal. For example, a value of 0.1 MHz would filter out any frequency components above this threshold.
IF: Analog [MHz]:
Defines the intermediate frequency (analog) used for signal mixing. Adjusting this value helps optimize the frequency range of the detected signal.
IF: Digital [MHz]:
Specifies the intermediate frequency for digital signal processing. This value can be fine-tuned to optimize the signal in the digital domain.
Base:
Refers to the zero level of the common-mode part of the signal. For example, a base value of 32768 indicates a certain offset level in the signal’s digital conversion process.
Dwell Time (0.5 us):
The time between each data point acquisition in the time domain. This value is locked by the manufacturer and cannot be adjusted by the user.
Processing Group Settings:
This group of settings deals with how the acquired NMR data is processed and visualized.
FFT Zero Filling:
A technique that adds zeros to the end of the acquired data before performing a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). Zero filling improves the resolution of the frequency spectrum.
Apodization:
The process of applying a window function to the time-domain signal before FFT. Different apodization functions can be used to reduce spectral leakage.
Auto Baseline:
Enables automatic baseline correction for the acquired spectrum. This is useful for removing any drift or offset in the baseline, which can interfere with accurate peak detection.
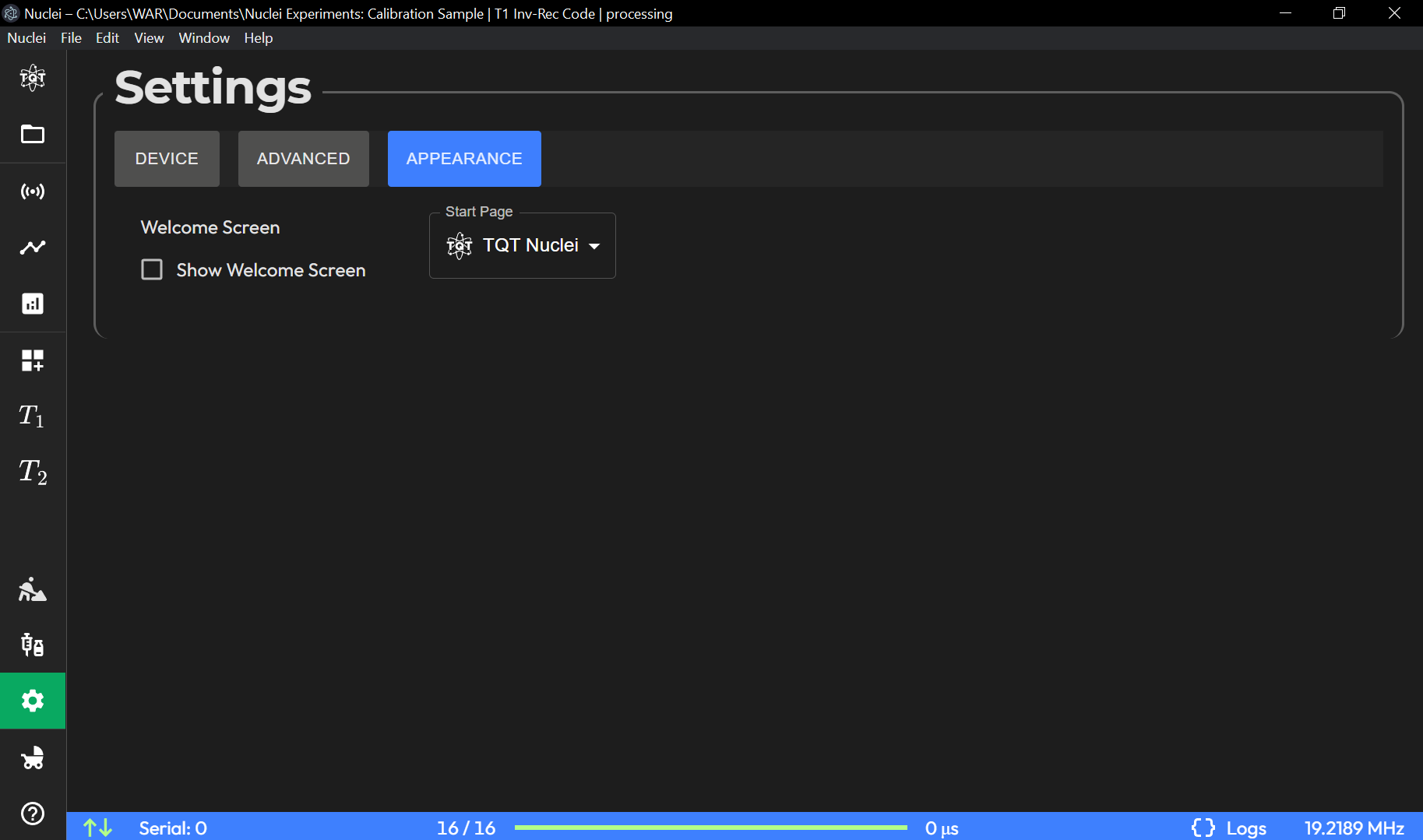
Appearance Subpage
The Appearance subpage allows users to customize how the application looks and behaves upon startup. This section is useful for personalizing the user experience and controlling the visual presentation of the application.
Welcome Pop-up Checkbox:
A checkbox that controls whether the welcome pop-up window appears when the application is started. Unchecking this option disables the welcome message.
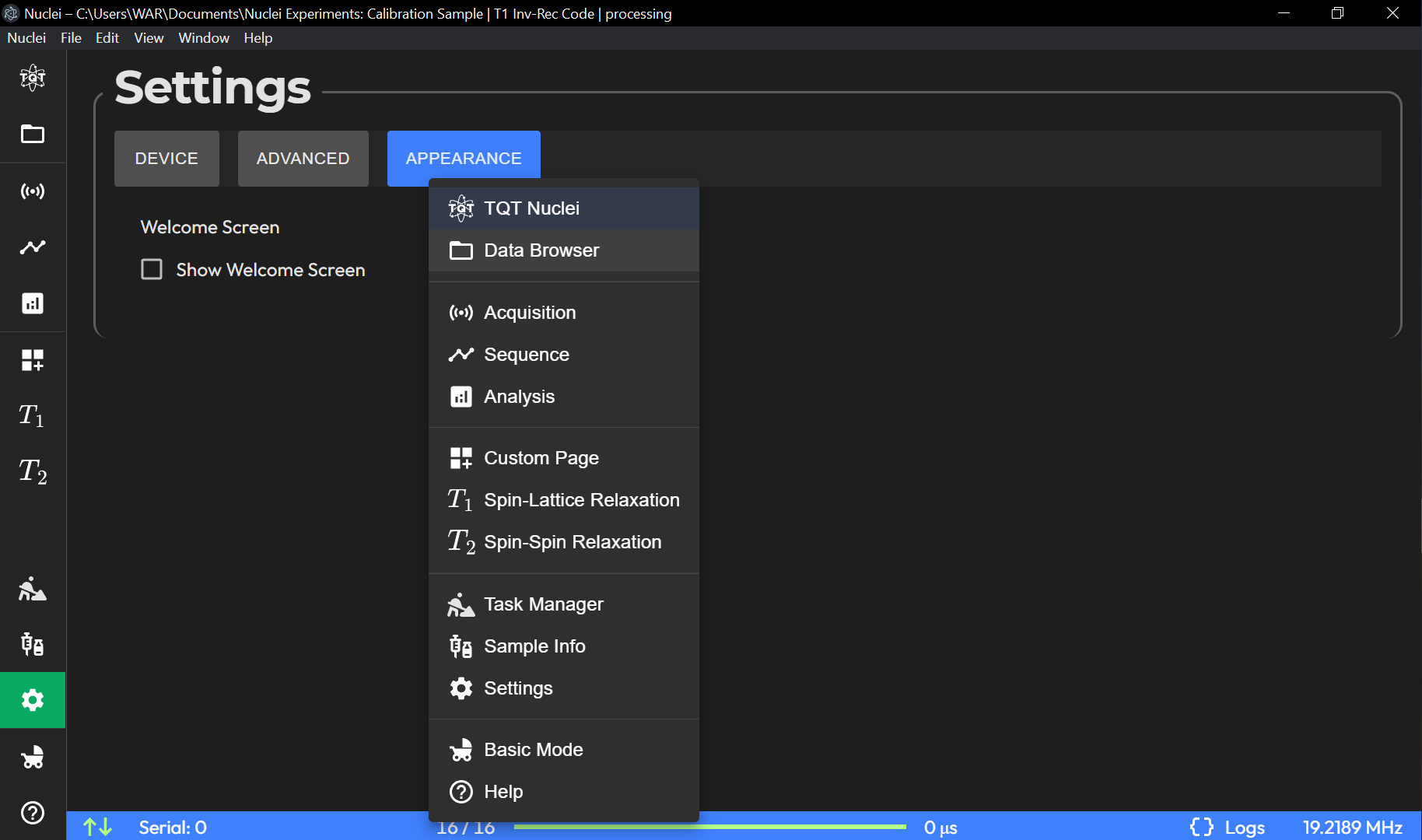
Start Page Selector:
Allows the user to choose which page will be displayed by default when the application starts. Any available page (such as HOME, ACQUISITION, DATA BROWSER, etc.) can be selected as the starting page. This feature helps streamline the user workflow by taking them directly to their most frequently used page.
Customization Example
A typical setup might involve the following adjustments:
In the Device subpage, the user sets the Frequency to 20 MHz, adjusts the Tx-1 Gain to match the sample’s sensitivity, and sets the Echo Time to 1000 µs for a standard CPMG experiment.
In the Advanced subpage, the user selects a Gauss FIR Filter with a window size of 128 units and sets the IF: Digital value to 0.5 MHz.
On the Appearance subpage, the user disables the welcome pop-up and sets the Start Page to ACQUISITION to save time during routine measurements.
These settings ensure an optimized workflow, improve signal acquisition, and offer a customized user experience.
Device Tab
Sensor Configuration: - Frequency: Sets the operating frequency of the NMR device (in MHz). - Ring Time: Defines the ring time in microseconds (µs). - Phase: Adjusts the phase angle in degrees (deg). - TX-1 Gain: Transmitter gain level as a percentage (%).
Receiver Settings: - RX-Gain: Controls the gain for the receiver, with a recommended range from 2% to 8%. - RX-Phase: Adjusts the phase for the receiver in degrees (deg).
Pulse Settings: Configures the durations for 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360° pulses in microseconds (µs).
Time Settings: Specifies the delay between repetitions in milliseconds (ms) and sets the echo time.
Advanced Tab
Analog Processing: Includes settings for FIR filtering, bypass options, and analog/digital IF settings.
Digital Processing: Configures zero-filling for FFT, apodization, and automatic phase/baseline settings.
Gradient: Placeholder for gradient settings.
Appearance Tab
Welcome Screen: Toggles whether the welcome screen is displayed at startup.
Menu Customization: Allows reordering or hiding features from the side menu to tailor the interface.